Brian Parker and Faculty Mentor: Benjamin Bikman-PDBIO
Introduction
The growing worldwide incidence of obesity and its associated pathologies, like type 2 diabetes, has received much deserved attention. However, despite this attention and substantial research efforts, little meaningful progress has been made in slowing or reversing the growing cost and trends of obesity worldwide.
As of 2008, almost 10% of medical costs in the United States were incurred due to obesity or other obesity-related diseases,i with the substantial amount of this cost stemming from the dramatically increased risk of diabetes with excess fat mass.ii According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than one third of adults in the United States are obese with the number increasing each year. As the cost of obesity related health care continues to grow, it is necessary to continue to search for novel, direct treatment options. While lifestyle and diet changes should continue to be studied, direct treatment options will be important to reverse the epidemic problem of obesity, which has already occurred. The proposed study may reveal such a treatment to address these concerns.
Methodology and Results
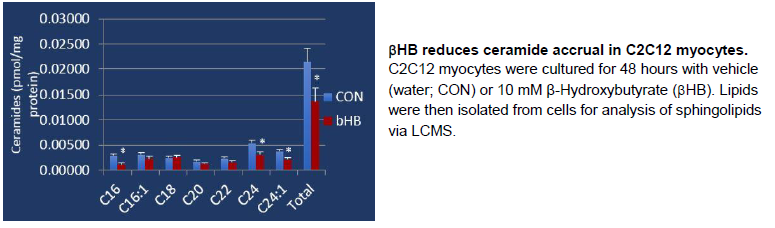
Cell culture—Murine myotubes (muscle cells) were incubated with -hydroxybutyrate (HB), then used for analysis. HB treatment increased muscle cell survival and proliferation, while also increasing mitochondria mass. Importantly, and perhaps reflective of its benefit to muscle tissue performance, HB increased ATP production over control conditions.

Discussion
Ketogenic diets are becoming increasingly popular in the United States, however there is substantial debate in the nutrition world concerning the efficacy in weight loss. Traditional nutritionists advocate that the most effective method for weight loss is to burn more calories than one intakes. Ketogenic nutritionists advocate that the most effective and healthy way to lose weight is to keep insulin low which will then induce fat metabolism.
Critics of ketosis often contest that it is a harmful state for the body to be in, but this notion is based off an incorrect comparison to ketoacidosis. In ketoacidosis, the ketones in the body are so elevated that they overcome the bicarbonate buffer which raises the blood pH to a toxic level which can rapidly destroy the body. In ketosis, the body is well within the bicarbonate buffer system. In fact, it is impossible to get into a state of ketoacidosis from diet, there must be a dysfunction in the body.
Conclusion
This study was done in hopes to determine the effect of ketosis on the body. As the results indicate, mitochondria in the muscle respond very well to ketones. The mitochondria were
healthier, produced more ATP and divided more readily.

i Finkelstein EA, Trogdon JG, Cohen JW, Dietz W. Annual medical spending attributable to obesity: Payer-and service-specific estimates. Health Aff (Millwood). 2009;28:w822-831
ii Kenneth E. Thorpe, Curtis S. Florence, David H. Howard and Peter Joski Trends: The Impact Of Obesity On Rising Medical Spending Health Affairs, no. (2004): doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.w4.480
