Sarah M. Buck and Dr. Steven Graves, Chemistry and Biochemistry
Na+/K+ ATPase, or sodium pump, is an integral protein that is essential in maintaining proper intracellular concentrations of Na+ and K+. The sodium pump exists in three isoforms which are present in varying numbers and relative distribution in different tissues. As the pump moves the ions in and out of the cell, it creates a cell membrane potential. When this potential decreases, muscle contracts. It is proposed that this may be a factor in the initiation or the sustaining of labor status. This study is concerned mainly with determining a possible correlation between sodium pump concentrations in pregnancy-related tissues and labor status.
Various pregnancy related tissues were obtained from healthy women both laboring and quiescent. These tissues include uteral myometrium, desidua, chorion, amnion, placenta, and fetal placenta. Tissues were compared using Western blot analysis to determine relative amounts of each isoform of the sodium pump.
Tissues were homogenized at physiological pH (7.4) followed by centrifugation to remove any remaining particles. Total protein concentration of each sample was determined using a Lowry protein assay. Equal amounts of protein from each sample were treated with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and separated using gel electrophoresis. The proteins were transferred from the gel and bound to a nitrocellulose membrane.
The membranes were probed for each isoform of the sodium pump using mouse monoclonal antibodies specific to a particular isoform. A second antibody with a chemiluminescent signaling group was then attached to the first. The luminescence signal, proportional to the amount of isoform present was detected by exposure to film. The image from the film was scanned into a computer and quantitized by analyzing the intensity of the signal.
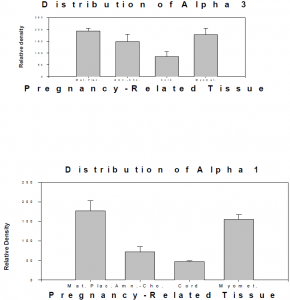
The study is not yet complete, but preliminary results indicate that some significant differences between tissue types are present1. For example, in a One-Way ANOVA Newman-Keuls’ Test, the maternal placenta contained significantly higher amounts of the alpha one isoform than amnion/chorion and myometrium. The myometrium also contained significantly higher levels of alpha one than the amnion/chorion and myometrium (see figure). The maternal placenta and myometrium also had significantly higher levels of alpha three than the cord.
Small sample groups also indicate that placenta from laboring women is higher in alpha two than quiescent placenta.
Acknowledgements: Hongyan Liang for significant help in collecting data.